A painting of a bustling medieval market street at sunset, with merchants, townsfolk, and soldiers on horseback.

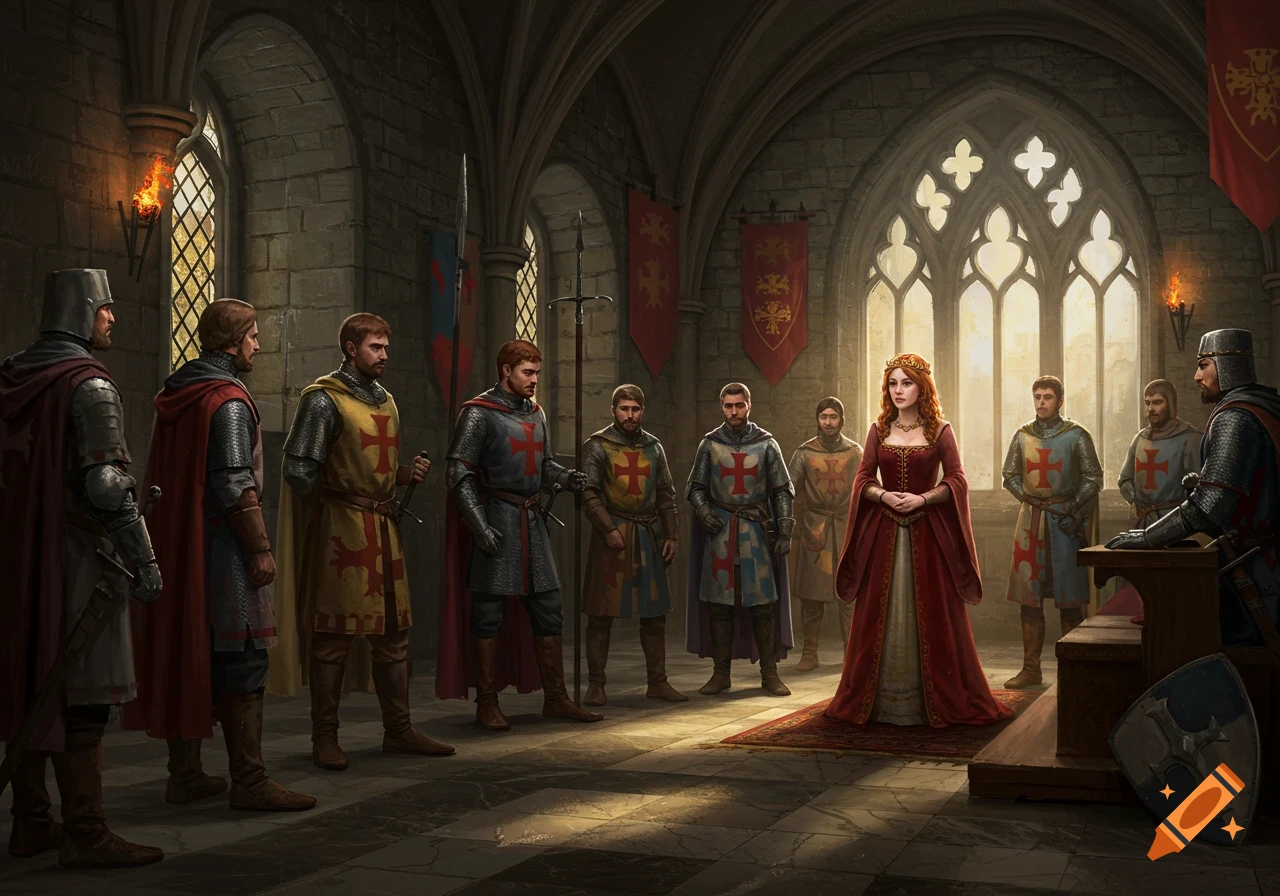
Since about 500 A.D., much of European society had been organized in a system of duties and exchanges based on land, war, and tradition. This intricate system was called feudalism. Europeans believed that everything, from the universe to the average household, was part of a hierarchy. • During the 1400s, feudalism gave way to the organization of nation- states. A growing middle class provided economic support for these new nations by producing and exchanging goods for money. As European trade continued to expand, nations faced economic competition with one another. See more